Chipmunks may seem like cute creatures darting through gardens and parks, but their burrowing habits, tendency to raid gardens, and ability to invade homes make them unwelcome guests. While they play a role in ecosystems, chipmunks can cause significant property damage if left unchecked. From tunneling under structures to chewing wires and ruining gardens, they pose a real hazard. This guide offers effective to help you get rid of chipmunks and prevent future infestations.
Table of Contents
- Why Are Chipmunks a Problem?
- Signs of Chipmunk Infestation
- Get Rid of Chipmunks with Natural Deterrents
- Get rid of Chipmunks with Trapping Techniques
- Get Rid of Chipmunks with Chemical and Commercial Repellents
- Modifying Your Yard and Garden
- Chipmunk-Proofing Your Home
- Professional Assistance
- Preventing Future Infestations
- Conclusion
Why Are Chipmunks a Problem?
At first glance, it may seem harmless to have a few chipmunks darting around your yard. But as their numbers grow, so do the problems they create. Understanding their impact can help justify taking steps to control their population.
Structural Damage
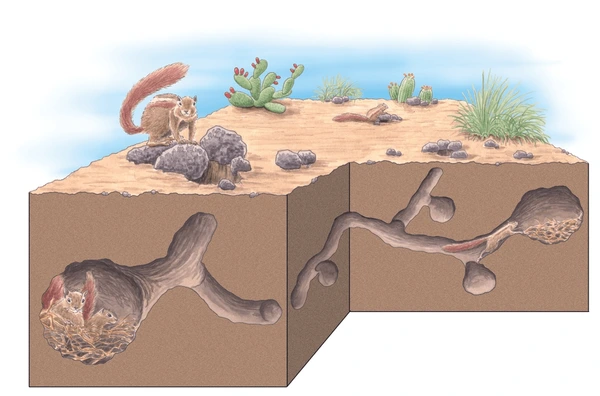
Chipmunks dig extensive burrow systems, often close to human structures. These burrows can undermine patios, sidewalks, driveways, and even building foundations. Over time, the weakened ground can cause cracking, sinking, or instability in these structures.
Garden Destruction
Gardeners frequently struggle with chipmunks raiding their crops. Chipmunks dig up flower bulbs, eat fruits and vegetables, and hoard seeds for their food caches. Their constant activity can undo hours of labor and result in significant financial losses for those who rely on their gardens for food or aesthetics.
Wiring and Insulation Damage
Inside homes, chipmunks can chew through electrical wiring, which creates fire hazards. They may also nest in attics or crawl spaces, tearing apart insulation and leaving droppings that contaminate your home.
Health Risks
While chipmunks are not aggressive, they can carry ticks, fleas, and other parasites that spread diseases like Lyme disease or salmonella. Their droppings and urine can also harbor harmful bacteria, posing a health risk to humans and pets.
Signs of Chipmunk Infestation
Detecting a chipmunk infestation early is key to preventing significant damage. Here are the signs to watch for:
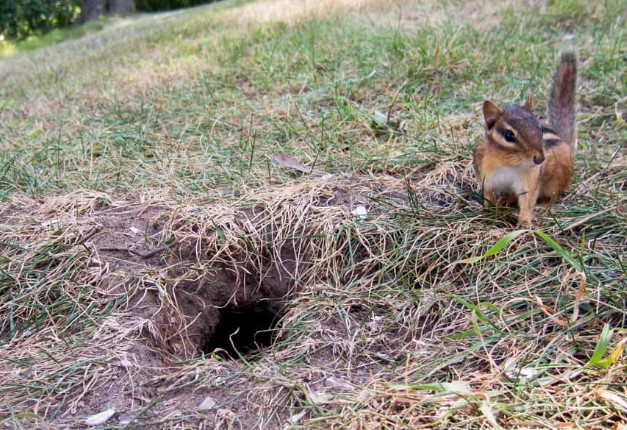
Burrow Holes
Chipmunks dig small, round holes (about 1–2 inches in diameter) to access their underground burrows. You might find these near your home’s foundation, in garden beds, or along walkways.
Plant Damage
If you notice plants uprooted or chewed, chipmunks may be the culprits. They often target bulbs, fruits, and young plants.
Noise
Chipmunks are diurnal (active during the day), so you may hear scratching, chirping, or rustling sounds if they’ve made their way into your home.
Tracks and Droppings
Chipmunk tracks are small, with four toes on the front feet and five on the hind feet. Their droppings are tiny, dark, and pellet-shaped, often found near burrows or food sources.
Frequent Sightings
Spotting chipmunks regularly around your property is a clear indicator of their presence.
Get Rid of Chipmunks with Natural Deterrents
If you prefer to manage chipmunks without using traps or chemicals, natural deterrents can be highly effective.
Scents and Sprays
Chipmunks have sensitive noses and are repelled by strong smells. Consider the following:
- Cayenne Pepper and Garlic Spray: Mix cayenne pepper, crushed garlic, and water to create a spray. Apply it around burrows, plants, and other chipmunk-prone areas.
- Predator Urine: Products that mimic the scent of fox or coyote urine can scare chipmunks away. These are available at garden centers.
- Essential Oils: Peppermint, citrus, and eucalyptus oils are known to repel chipmunks. Soak cotton balls in these oils and place them near entry points or gardens.
Physical Barriers
- Use hardware cloth or wire mesh to cover garden beds, flower bulbs, or any other areas where chipmunks are causing damage.
- Install mesh screens over vents, chimneys, and crawl spaces to block access.
Ultrasonic Devices
Ultrasonic repellents emit high-frequency sounds that irritate chipmunks while being inaudible to humans. Place these devices near burrows or problem areas for a non-invasive solution.
Get rid of Chipmunks with Trapping Techniques
Trapping is one of the most effective methods for removing chipmunks, but it must be done responsibly to ensure the well-being of the animals and compliance with local laws.
Choosing a Trap

- Live traps: These cage or box traps capture chipmunks alive, allowing for humane relocation. They are a great choice for those seeking to avoid harm.
- Snap traps: These are common lethal traps that kill chipmunks quickly by snapping their neck or back when triggered. If you choose snap traps, place them in areas that minimize risk to non-target animals and pets.
- Bucket traps: A DIY solution, where chipmunks fall into a bucket after being lured by bait. If designed with a drowning method, this will kill the chipmunk, but it’s essential to execute this technique quickly and humanely, as prolonged drowning is considered inhumane.
- Multiple-catch traps: These traps capture several chipmunks at once, allowing for relocation or removal. Some variations can be lethal, so ensure you select one that suits your ethical preferences.
Baiting the Traps
- For live traps, use peanut butter, sunflower seeds, or fruits like apples, bananas, or berries to attract the chipmunks.
- For lethal traps, consider using the same types of bait as you would for live traps, but ensure the traps are positioned carefully to prevent accidental harm to non-target species.
Setting and Monitoring Traps
- Location: Place traps near active burrows, garden beds, or areas where chipmunks are frequently seen. Look for signs such as droppings or chewed plants to help you pinpoint the best spots.
- Frequency: It’s important to check both live and lethal traps frequently. With snap traps, ensure they’re set correctly and check them often to minimize the suffering of the chipmunk and prevent trapping non-target animals.
Releasing or Disposing of Chipmunks
- For live traps: Relocate chipmunks at least 5–10 miles away in a wooded or rural area. Be sure to check local wildlife regulations to ensure you comply with any relocation laws.
- For lethal traps: If the chipmunk is killed, dispose of the body appropriately. Some localities have guidelines on how to handle and dispose of trapped animals.
Legal Considerations
- Check local laws: In some regions, the use of lethal traps may be restricted, and relocation of captured animals may also require permits. Always verify that your trapping method complies with local wildlife laws to avoid penalties.
Whether you choose a live trap for humane relocation or a lethal trap, it’s essential to take all necessary precautions to ensure both the safety of the chipmunk and the responsible execution of trapping methods.
Get Rid of Chipmunks with Chemical and Commercial Repellents
If natural methods and trapping do not fully address your chipmunk problem, chemical and commercial repellents can offer an additional layer of protection. However, it’s essential to use these products responsibly to minimize risks to the environment, pets, and other wildlife.

Granular and Spray Repellents
- Granular Repellents: These repellents are designed to be scattered around areas with high chipmunk activity, such as burrows, garden beds, and pathways. The granules create an unpleasant odor or taste that deters chipmunks from approaching or digging in those areas. Choose products that contain natural ingredients like peppermint oil, cinnamon, or garlic, which chipmunks find offensive.
- Application Tips: Reapply granular repellents after rain or heavy watering, as moisture can wash away the scent and reduce effectiveness.
- Spray Repellents: These are often applied directly to plants, structures, or areas where chipmunks are entering your home or garden. Look for spray repellents that contain active ingredients like capsaicin (from hot peppers) or putrescent egg solids, both of which are natural deterrents.
- Application Tips: Focus on areas where chipmunks are most active, such as along fence lines, around tree trunks, or near burrow entrances. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid damage to plants or surfaces.
Rodenticides: A Cautionary Note
- Rodenticides: While these products are designed to kill rodents, they should be considered only as a last resort due to the significant risks they pose. Rodenticides can be harmful to non-target animals, including pets, birds, and wildlife, who may accidentally ingest poisoned bait or contaminated prey.
- Environmental Concerns: Rodenticides can also pose a long-term environmental threat, especially if chipmunks or other rodents die in hidden areas, leading to decomposition and attracting scavengers. This can cause a ripple effect in the ecosystem, with poisoned predators consuming the dead rodents.
- Guidance for Use: If you decide to use rodenticides, always follow the product’s instructions carefully. Consider working with a professional pest control service to ensure proper placement and minimize hazards to pets and other animals. In many cases, professionals will opt for safer alternatives or targeted baits that reduce risks.
Eco-Friendly and Non-Toxic Alternatives
- Essential Oils: Chipmunks are repelled by certain essential oils, such as peppermint, cinnamon, and eucalyptus. These can be diluted and sprayed around entry points, or you can soak cotton balls and place them near burrows. Regular reapplication is necessary to maintain effectiveness.
- Predator Urine: Another deterrent that some homeowners use is predator urine (such as fox or coyote urine). This creates the illusion of danger and encourages chipmunks to relocate.
Important Considerations
- Effectiveness Varies: While chemical repellents can work, their effectiveness can vary based on the severity of the infestation, the local environment, and the chipmunks’ behavior. Often, a combination of repellents, trapping, and exclusion techniques yields the best results.
- Use Caution Around Pets: Always take care when using chemical repellents or rodenticides, particularly if you have pets. Many repellents are safe for pets, but others can be toxic if ingested. Ensure that products are clearly marked as safe for animals if used in areas where pets roam.

Modifying Your Yard and Garden
Making your property less attractive to chipmunks is a proactive way to prevent infestations.
Removing Food Sources
- Clear away fallen fruits, nuts, and seeds from your yard regularly.
- Use chipmunk-proof bird feeders with seed catchers to minimize spilled birdseed.
- Store pet food, grains, and garbage in sealed, sturdy containers.
Clearing Shelter Areas
- Trim shrubs and bushes that provide cover for chipmunks.
- Remove woodpiles, rock piles, and debris, as these make ideal hiding spots.
- Replace organic mulch with gravel or stone, which chipmunks find less appealing.
Landscaping with Repellent Plants
Incorporate plants that naturally repel chipmunks, such as daffodils, alliums, or fritillaries. These plants are less likely to be targeted.
Chipmunk-Proofing Your Home
Chipmunks often seek shelter in homes, garages, sheds, and other structures, particularly as the weather cools. To prevent these industrious rodents from entering, it’s important to take a proactive approach by sealing entry points, reinforcing vulnerable areas, and regularly inspecting your property for new signs of activity.
Seal Potential Entry Points
- Thorough Inspection: Start by carefully inspecting your home’s exterior for any gaps or cracks around doors, windows, vents, and utility pipes. Chipmunks can squeeze through surprisingly small openings—anything larger than 1/4 inch should be sealed.
- Effective Sealants: Use durable materials like caulk, steel wool, or hardware cloth to fill in cracks and crevices. For larger gaps, mesh or foam fillers work well. Steel wool is particularly effective for sealing around pipes since it’s difficult for chipmunks to chew through.
- Close Gaps Around Foundations: Check the foundation of your home for cracks or holes. These are common entry points, especially in older homes. Use concrete patching materials to close any significant gaps.
Reinforce Vulnerable Areas
- Vent and Chimney Protection: Install mesh screens or chimney caps to cover vents and chimneys. Chipmunks can easily climb walls and enter through these openings, so adding barriers ensures they can’t gain access.
- Secure Window and Door Frames: Ensure weather stripping is intact and replace any worn-out strips around doors and windows. A tight seal keeps chipmunks from slipping through gaps, especially in areas prone to drafts or wear and tear.
- Protect Other Entry Points: Don’t forget areas like attic vents, dryer vents, or air conditioning units. Install fine mesh screens or specialized vent covers to block access.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
- Routine Checks: Perform regular checks around the perimeter of your home, especially after heavy storms or during seasonal changes. Look for new burrows, gnaw marks, or signs of reentry like droppings.
- Monitor Known Hotspots: Keep an eye on areas where you’ve previously found signs of chipmunk activity. If you notice new burrows, fresh gnawing, or disturbed soil near these spots, take action immediately to reinforce those areas.
Additional Preventative Measures
- Remove Outdoor Attractions: Trim back shrubs and bushes near the home to reduce cover and eliminate easy access to your roof or foundation. Also, remove any food sources like bird feeders or pet food that might draw chipmunks to your property.
- Seal Shed and Garage Openings: If chipmunks are entering your garage or shed, make sure to seal any gaps around the door and windows. Consider installing a door sweep or weather stripping to create an airtight seal.
- Roof Inspection: Chipmunks are excellent climbers, so be sure to check your roof for any vulnerable areas. Seal off vents or gaps in the roofline, and repair any missing shingles or holes that could serve as an entry point.
Professional Assistance
If DIY methods fail or the infestation is severe, professional pest control services can provide effective solutions. Professionals can:
- Identify entry points and burrows.
- Use advanced traps and deterrents.
- Safely and legally remove chipmunks from your property.
Preventing Future Infestations
To ensure chipmunks don’t return, take proactive measures:
- Keep your yard clean and free of debris.
- Maintain physical barriers and deterrents, such as mesh screens and repellents.
- Regularly inspect for signs of chipmunk activity.
Conclusion
Chipmunks may be charming in small numbers, but they can become a major nuisance when they invade homes and gardens. By using natural deterrents, physical barriers, humane traps, and preventative measures, you can effectively get rid of chipmunks and keep them from returning. Staying vigilant and acting early will help you maintain a chipmunk-free property while minimizing harm to these animals and the environment.